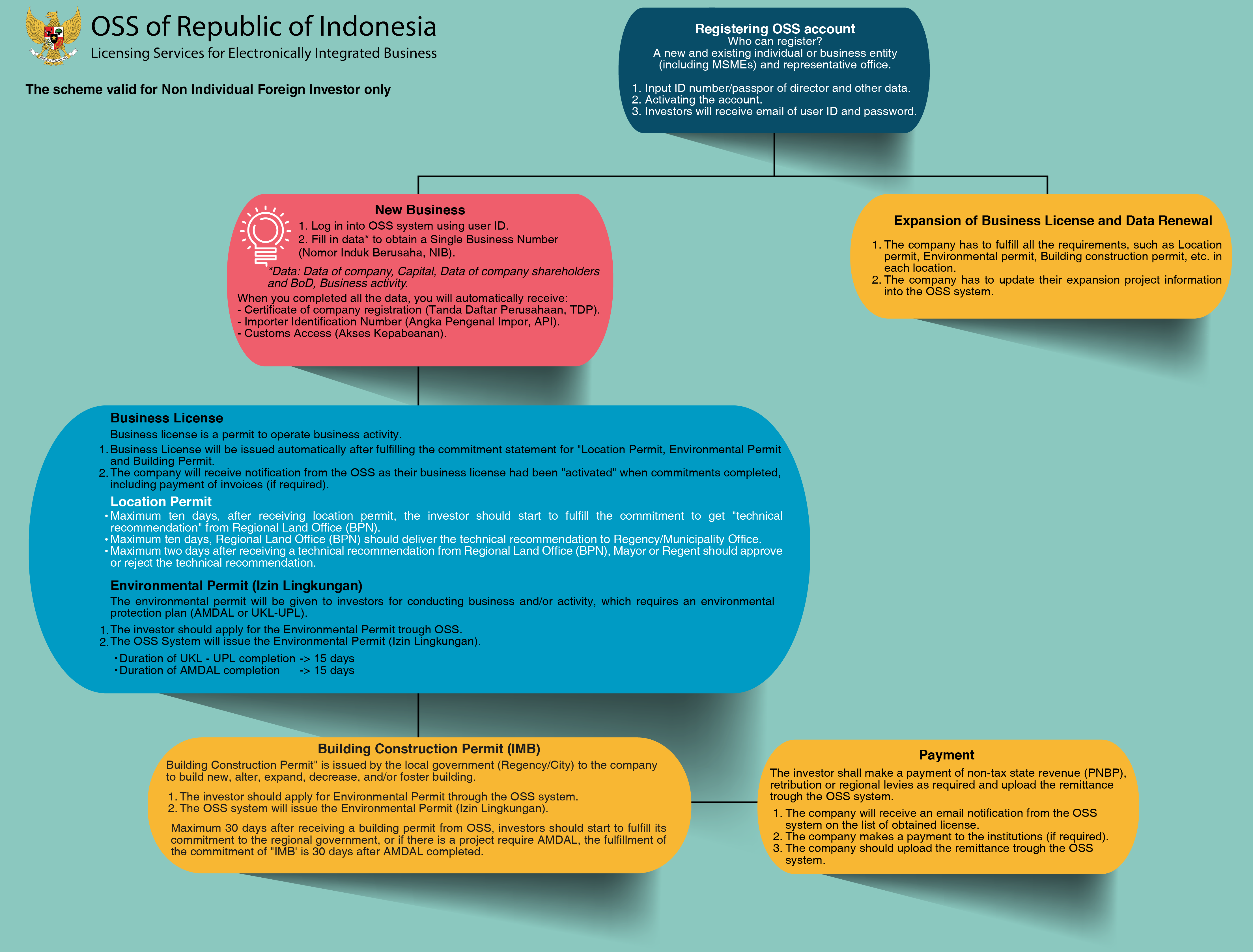
Step by Step New Investment or Expansion
How to Invest
Find out how to invest in Indonesia and learn more about applicable government regulations and policies
Step #1
Deed of Establishment of the Indonesian-based Company (PT. PMA):
- At least 2 shareholders are required (A Director and A Commissioner);
- The Director needs to reside in Indonesia;
- Minimum capital investment value is IDR 10 billion in each business field.
Step #2
Check the Indonesian Positive Investment List:
- To help you identify which business fields which are open to foreign investment with some limitations, open to foreign investment with a compulsory partnership with Small & Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) or completely closed off to foreign investments;
- Foreign investors can own 100% ownership without conditions for business fields which are not on the list;
- Foreign investment must be in the form of a legal entity domiciled in Indonesia.
Step #3
Registering OSS account
Who can register? A new and existing business entity (FDI) and representative office.
Step #4
Introduction to Risk-Based Approach Business Licensing:
In an attempt to improve the Indonesian business climate, by means of simplifying the procedure and speeding up the process, the Government of Indonesia introduces a Risk-Based Approach for Business Licensing.
The novel approach classifies businesses into four risk categories – ranging from low, medium-low, medium-high, and high – based on the consideration of: (1) Risk level of the business activities; (2) Scale of the business; (3) Hazard level assessment and potential for the occurrence of any hazards; (4) The size of the land area.
The risk-level is determined upon the completion of data on the OSS system and will set out the types of document required to start business activities which is classified into two stages: (1) The preparation stages, and (2) The commercial and operational stages.
Step #4.1
Risk-Level
- Low risk : the Single Business Identification Number (Nomor Induk Berusaha, NIB) can be used to start conducting commercial and operational activities;
- Medium-low risk: the NIB and the Certificate of Standard (self-declared) are required to obtain the business license that serves as a legal evidence to start conducting commercial and operational activities;
- Medium-high risk: the NIB and the Certificate of Standard (self-declared) are used to start conducting activities in the preparation stages. The business license is required for the business entity to start conducting commercial and operational activities, and the license will be issued upon the verification and validation of the Certificate of Standard.
- High Risk: the NIB and the Certificate of Standard (self-declared) are used to start conducting activities in the preparation stages. The business license is required for the business entity to start conducting commercial and operational activities, and the license will be issued upon the verification and validation of the Government and/or certain authorities approval depending on the business sectors.

Step #4.2
Single Business Identification Number (NIB)
- Log in into OSS using the registered user ID;
- Fill in data to obtain a Single Business Number (Nomor Induk Berusaha, NIB) and have the business activities risk-level assessed;
When the company completed all data, it will receive the NIB, which can also be used as:
- Certificate of company registration (Tanda Daftar Perusahaan, TDP);
- Importer Identification Number (Angka Pengenal Impor, API)
- Customs Access (Akses Kepabeanan).
Step #4.3
Business License
- Business License is issued upon the submission of the required documents based on the risk-level;
- The company will receive notification from the OSS if all commitments completed, including payment of invoices (if required);
- Business License is the legal evidence for the business entity to start conducting commercial and operational activities;
- The progress of those permits will be monitored by the Ministry of Investment / Indonesia Investment Coordinating Board (BKPM) regularly every 3 months.
Concerning the issuance of Government Regulation (GR) No. 24 of 2018 on Electronic Single Submission System (Online Single Submission/OSS), we herewith inform that all registration for new investment and business expansion is now done through One Stop Service Center website to serve investors who need information, assistance, and consultation.